Will Changing a Single Nucleotide Always Change the Amino Acid
Normal hemoglobin is a tetramer consisting of two molecules of β-globin and two molecules of α-globin. In this case most.

Solved A Change Of One Nucleotide In A Dna Sequence May Change The Sequence Of Amino Acids In The Protein Does This Always Happen Why Or Why Not Explain How A Change In
Another way a nonsynonymous mutation can occur is if the point mutation changes the single nucleotide into a codon that does not translate into the same amino acid.
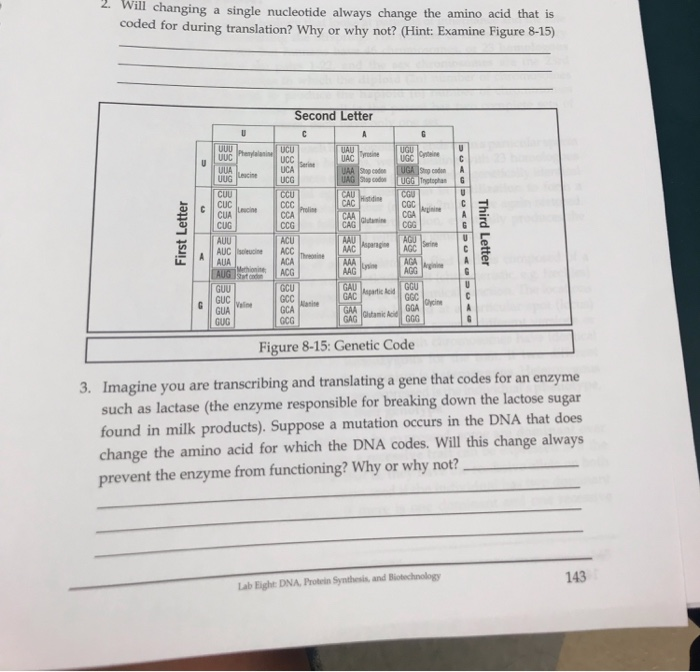
. With base substitution mutations only a single nucleotide within a gene sequence is changed so only one codon is affected Figure 1. In sickle-cell disease as a result of a single amino acid change the mutant. Relationship between codon base change and amino acid polarity or hydrophobicity.
Sometimes a change in a nucleotide does NOT change the amino acid and therefore the protein because some amino acids have more than one set of 3 nucleotides that code for them. If a single nucleotide is changed then the codon coding the specific amino acid will also change and some other amino acid will be coded which will further lead to the change in the peptide. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the.
Only a single codon in the gene sequence is. When comparing the original strand of DNA to the mutated strand of DNA how many. Changing a single nucleotide will change the amino acid sequence which can impact how the protein it forms will look and act.
Where in the cell do the following occur. This deceptively simple change in turn can affect the structure or function of a. The rules that allow amino acids to be interchangeable specify that a.
Idiosyncratic amino acids - there are few similar amino acids that they can mutate to through single nucleotide substitution. Missense mutations are insertions or deletions of one or more base pairs if the number of base pairs is not a multiple of 3 that disrupt the coding of a protein. Most of these small changes dont have a.
No changing the DNA sequence particularly if the change is only in one nucleotide does not necessarily result in a different amino acid in the protein sequence. Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence.
Leucine is an example of a typical amino acid. A Changing a single nucleotide base on the mRNA chain can lead to one of three results. If the mutation causes a premature.
Almost always yes but different sequences of nucleotides can sometimes result in the same or correct amino acid being transcribed. A single change in the DNA nucleotide sequence of a gene can cause the wrong amino acid to be produced. When the change in codon does not affect which amino acid it corresponds to.
If the mutation is synonymous ie does not change the nature of the amino acid then translation rates or mRNA half-life may be affected.

Solved 2 Will Changing A Single Nucleotide Always Change The Chegg Com

Types Of Variants Garvan Institute Of Medical Research

Substitution Dna Mutation Definition Examples Expii
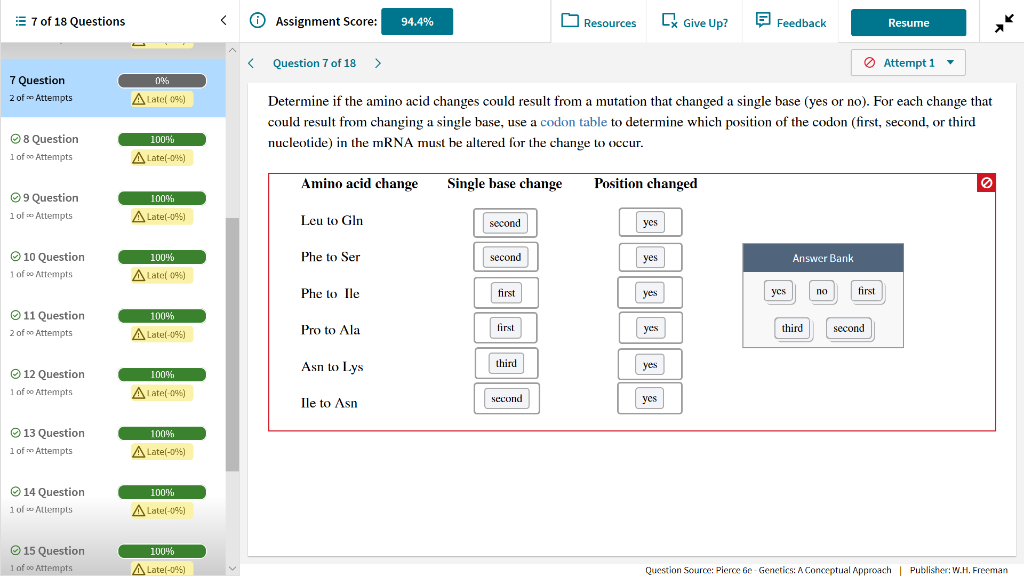
Solved 7 Of 18 Questions Assignment Score 94 4 Resources Chegg Com
No comments for "Will Changing a Single Nucleotide Always Change the Amino Acid"
Post a Comment